Welcome to the 2nd article in our educational, informative, and fun series of deep dives into the world of XCM and Cross-Chain NFTs. In the Polkadot ecosystem, XCM (Cross-Consensus Messaging) offers two primary models for token transfers: Teleport Transfer and Reserve-Based Transfer.
This article will explore these two models and provide an understanding of NFT XCM's own transfer mechanism, the differences between bridges and XCM, and the filling in the gaps for XCM to enable NFT transfers.
Quick Re-Cap
XCM, Polkadot’s Cross-Consensus Messaging, enhances interoperability by connecting parachains and projects alike, giving them and users the best user experience when transferring assets and/or tokens.
However, this was only available for Fungible Tokens (FTs), e.g. transferring tokens, but not unique assets, thus it was not possible to transfer NFTs between projects and parachains on Polkadot.
Unique Network, an NFT-driven parachain on Polkadot, submitted a development proposal on Polkadot’s Open Governance outlining the work and scope to fulfill Gavin Wood’s interoperability dream and develop what we know today as NFT XCM.
NFT XCM is an initiative developed and led by the Unique Network team, designed to simplify the transfer of NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) across Polkadot parachains and projects that will unleash the capabilities for the next generation of Web3.
NFT XCM is needed to enable trustless and efficient Cross-Chain transfers of NFTs.
Current Capabilities & Limitations of XCM
The Teleport Transfer and Reserve-Based Transfer are two approaches widely utilized across the Polkadot ecosystem, each with its distinct mechanism, trust requirements, and various use cases.
Below, we will explore these methods and their advantages and disadvantages to get a better understanding of how XCM works on Polkadot.
The First Approach: Teleport Transfer
This approach involves the complete "movement" of an asset from one chain to another.
Mechanism:
- The asset is burned on the source chain.
- A new asset, equivalent to the original, is created on the target chain.
Advantages:
- More autonomy in managing the asset on the target chain.
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to organize truly trusted interactions.
- Requires complex coordination between chains to ensure consistency and continuity.
The Second Approach: Reserve-Based Transfer
In this approach, the asset remains under the control of the source chain, which acts as its "reserve". When transferring an asset to another chain, it remains on the source chain but is taken out of use, and a "certified copy" of this asset is created on the target chain.
Mechanism:
- The asset is moved between accounts within the source chain. It is moved to an account controlled by the target chain (its so-called “sovereign account”).
- A derivative asset is created on the target chain, referencing the original.
- When returning the asset back to the source chain, the derivative on the target chain is "burned" (or is made inaccessible and non-interactable, i.e., equivalently burned), and the original is withdrawn from the target chain’s sovereign account and deposited to the beneficiary’s account.
Advantages:
- Simplified management, as the reserve remains on the source chain.
- Control over the uniqueness and history of the asset is maintained.
Disadvantages:
- Limited flexibility in managing the asset's properties on the target chain.
Current Practices
The Reserve-Based approach is the most commonly used model in practice.
For example, parachains use this method to exchange their native tokens. This includes transferring UNQ tokens between Unique Network (the reserve chain for UNQ) and Acala or moving USDT from AssetHub (the reserve chain for USDT) to other chains.
Similarly, DOT (the native token for Polkadot) is transferred from the Relay Chain (its reserve chain) to non-system chains using this approach.
On the other hand, Teleport Transfers are predominantly used among Polkadot’s system chains—chains developed by the Parity team, such as the Relay Chain, AssetHub, and BridgeHub. These transfers rely on complete mutual trust between chains, allowing assets to be destroyed on the source chain and recreated on the target chain.
While Teleports are theoretically feasible between any pair of parachains, practical adoption has been rare due to the stringent trust requirements. Most parachains instead trust other chains only concerning the assets natively created on those chains, making the Reserve-Based model the default choice.
The same framework applies to transferring NFTs using XCM. For NFTs, the Reserve-Based model was selected for initial implementation for two key reasons:
- It aligns with the most prevalent practices among parachains.
- It is technically simpler to implement and integrate.
The next step in this evolution is exploring the Teleport model for NFTs, planned for 2025, unlocking further potential use cases and benefits.
Both models have unique advantages and challenges, from trust requirements to flexibility in managing assets across chains.
For a deeper dive into these models and their implications for NFTs, watch our talk at Sub0 2023.
Understanding the NFT XCM Transfer Mechanism
Imagine you have a unique comic book. You store it in a safety deposit box in Bank A.
You want your comic book to be transferred to another country and to use it there. To do that you need to place it in Bank B. After that, you can showcase it, put it to a specific auction, or even get it appraised by a specialist and get a loan based on the comic’s value.
Instead of physically retrieving the original, moving it to another bank, and placing it in another safety deposit box there (Teleport Transfer), Bank A and Bank B decide to make an agreement.
- Bank A transfers your asset to another security box owned by Bank B. But this security box is located within Bank A. The asset never leaves Bank A physically but is now owned by Bank B.
- Bank B issues you a certified copy of your original comic book. Now you can use it in Bank B just as you would the original.
- The original still remains in the safety deposit box in Bank A. The owner of the copy can be confident in its security and that it is kept there; there will be no other copies or actions with the original until they decide to destroy the copy and retrieve the original.
Connection to Polkadot
- Reserve Chain (Bank A): Your NFT remains on the source parachain, (where it was created) and is "reserved" and protected. The owner's address in this network is the safety deposit box; the NFT is the asset within it. The actual transfer of the asset when using XCM occurs only within the reserve chain between the original owner’s account and the target chain’s sovereign account (it is an account on the reserve chain that is controlled by the target chain), ensuring maximum security and stability of the entire system.
- Target Chain (Bank B): On the target parachain, a "representation" of your NFT is created—this is another NFT that unambiguously references the original, with the reliability of this connection ensured by the XCM agreement.
Thus, Reserve-Based Transfer provides a secure and efficient way to transfer NFTs between different parachains, similar to how banks manage clients' valuables through a system of trusted copies and certificates.
Differences Between Bridges and XCM
Bridging and XCM transfers share a similar goal—enabling cross-chain interactions, but differ significantly in their approach and have certain advantages and trade-offs.
Bridging enables cross-chain communication between technically diverse networks like Polkadot and Ethereum. Bridges allow these chains to acknowledge each other and trust each other’s finalized states, paving the way for many applications like asset swaps and chain migrations.
XCM, as we already looked at above, is Polkadot native and enhances interoperability by connecting parachains and projects alike.
Purpose:
- Bridging: Primarily used to transfer assets (e.g., tokens, chain migrations) between entirely different blockchains (e.g., Polkadot to Ethereum). They focus on enabling interoperability between ecosystems with different technologies. An example of a popular bridge serving this purpose is Hyperbridge. See Snowbridge for another example.
- XCM: A common format amongst different consensus systems to communicate between parachains and projects on Polkadot. Designed for deep interoperability within a shared ecosystem (E.g., transferring tokens like ASTR, or PLMC to another parachain).
Trust Model:
- Bridging: Typically relies on third-party validators or external mechanisms to transfer assets or data between two blockchains.
- XCM: Operates natively within the Polkadot ecosystem using shared security provided by the Relay Chain. Since parachains are already secured by the Relay Chain, XCM communication does not require external validators, making it inherently more trustless and secure.
Architecture and Native Support:
- Bridging: Connect blockchains that have separate consensus mechanisms (e.g. Ethereum or Solana).
- XCM: Designed specifically for Polkadot and Kusama parachains. It provides a standardized protocol for native message passing, allowing parachains to communicate seamlessly without the need for additional infrastructure.
Filling the Gaps: XCM Enhancements for NFT Transfers
XCM is an agreement on the mechanism and rules for transferring assets between blockchains in the Polkadot ecosystem. XCM derives from 3 main key system components:
- The Chain Asset Manager
- XCM itself
- The Asset Transactor
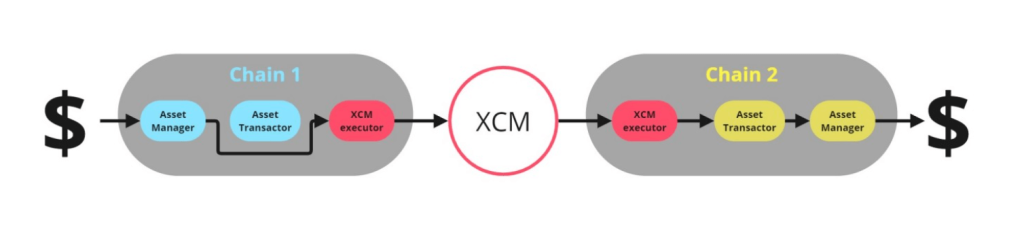
The Chain Asset Manager exists alongside XCM and is a set of functionalities of each specific blockchain, what assets it can store, what actions can be performed, and what unique ways to do it. In the Polkadot ecosystem, this can be a combination of pallets, modules, and other components of each particular chain.
A special component, the Asset Transactor, was developed and effectively allows the packing and unpacking of NFTs – the first stepping stone into what we see today as NFT XCM. It acts as a “translator” between the XCM language and the specifics of each parachain.
However, it’s important to note, that XCM would only work if each parachain built the Asset Transactor themselves on their projects.
In the future, we plan to generalize to allow NFT transfers on all other parachains that wish to utilize this tech and send NFTs across different parachains, in addition to building out a UI platform for viewing NFTs and executing XCM transfers.
Next Up: XCM’s Components & How it Works
Coming up next in our NFT XCM educational series, we will explore XCM’s components, its structure and a dive deep into how it all works. We encourage you to stay tuned on our social media, such as X for more details and check out our official blog page!
Final Thoughts
NFT XCM paves the future for seamless interoperability for NFTs on Polkadot, and Unique Network is excited to be driving this next-gen technology for years to come to unlock endless opportunities for limitless NFT innovation.
This innovation fortifies interoperability, enhances trust, and fuels the next wave of NFT development on Polkadot – bringing NFTs 2.0 closer than ever before.
Join the Unique Ecosystem!
Unique Network is the number one next-generation NFT chain for Polkadot and Kusama, bridging the gap between Web2 and Web3 by giving you all the necessary tools and platforms to achieve your dreams as easily as possible.
Step into the world of Web3 with the NFTs 2.0 CodeCraft Grant Fund, complete with unlimited advanced NFT features built for today and the future. Build your unique dApp or Micro dApp, join a community of developers, and get direct support for your project.
Learn more about the dApps and projects actively using Unique Network today:
|
dApp |
Description |
Visit Page |
|
Conor Daly Insider Pass |
A unique Digital Insider Pass to promote Fan Engagement in Web3 and bridge non-crypto natives to the Web3 world. |
|
|
Sovereign Nature Initiative |
One-of-a-kind Proof of Attendance Badge on the Blockchain, that evolves into an exclusive DOTphin NFT. |
|
|
DED Games |
A brick-breaking game, showcasing NFTs to gamers as they try to complete challenges and reach the leaderboards. |
|
|
Forever Has Fallen |
Bringing Bounty Hunter Tickets as NFTs to gamers, unlocking challenges, riddles, and an exclusive lair to those who seek. |
Stay Up To Date
Follow Unique Network to get all the latest information, and join us to start your own unique, development journey:
- Follow us on Twitter @Unique_NFTchain
- Join our community Telegram
- Join our community Discord
- For Developer Queries: [email protected]
- For Any Other Queries: [email protected]









 by
Unique Network
by
Unique Network